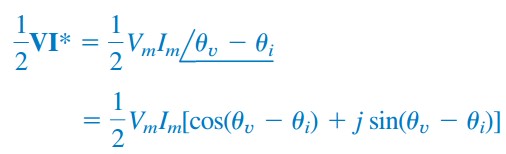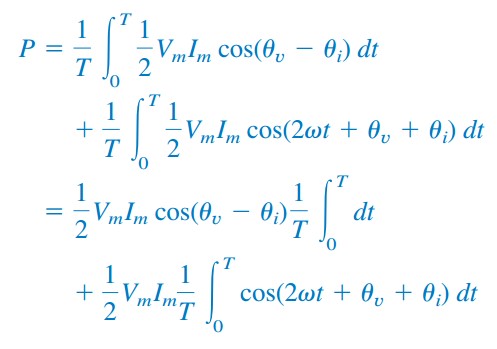Fabulous Formula For Instantaneous Power
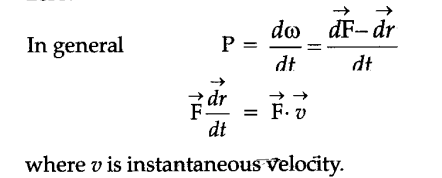
Therefore the average power P for a periodic instantaneous power p is given by P 1 T 1 t1T 1 t1 p dt 4 P 1 T 1 t 1 t 1 T 1 p d t 4 Where t1 is arbitrary.
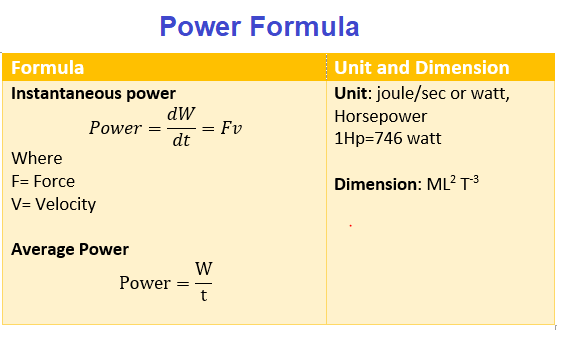
Formula for instantaneous power. If you differentiate work done wrt time it will be the instantaneous power. The equation P W Δt only works for average power. 222 Part a 332 Solving for Δt.
F P g F g v inst cosθFv y cosθF0cosθ0 Instantaneous power delivered by the force of gravity at the very start Note. Calculating the instantaneous power equation for an AC circuit is however not so straightforward. The instantaneous power equation for a DC circuit can also be expressed by.
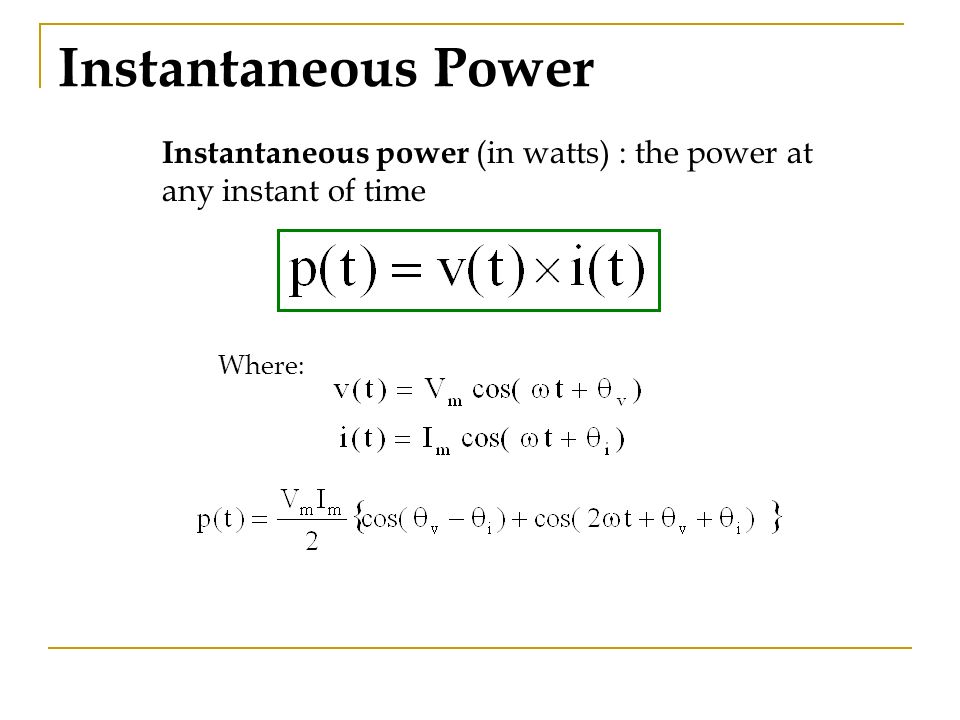
This is just a few minutes of a complete course. P t v t i t The above expression defines power at any instant of time and is the rate at which an element absorbs energy in watts. So the instantaneous power in a single phase circuit varies sinusoidally.
So one watt which is the rate of expending energy at one joule per second will be equal to the volt-ampere product of one volt times one ampere. Pt vtit VIcosωt θVcosωt θI 2 This expression is further simplified with the aid of the trigonometric identity. Instantaneous power is the product of the instantaneous voltage across a circuit element and the instantaneous current through it.
Look that the instantaneous power frequency is twice the frequency of voltage or current. A circuit element dissipates or produces power according to P IV where I is the current through the element and V is the voltage across it. In one complete period the average of oscillating term is zero.
Since the current and the voltage both depend on time in an ac circuit the instantaneous power pt itvt is also time dependent. 532 Alternate solution to part a 633 Average vs. Instead both voltage and current are time-varying sinusoidal waveforms.